Update time : 2025-08-20 Publisher:Zhengzhou Hanke Machinery
The "single-bin blending silo" is actually a silo used to complete the blending of powdered organic fertilizer. The key is to control the amount of each blending and the uniformity of the mixture. The operation logic is very simple. To put it simply, it's about "blending the material in one step". Here, Zhengzhou Hanke Machinery will tell you the steps in plain language:
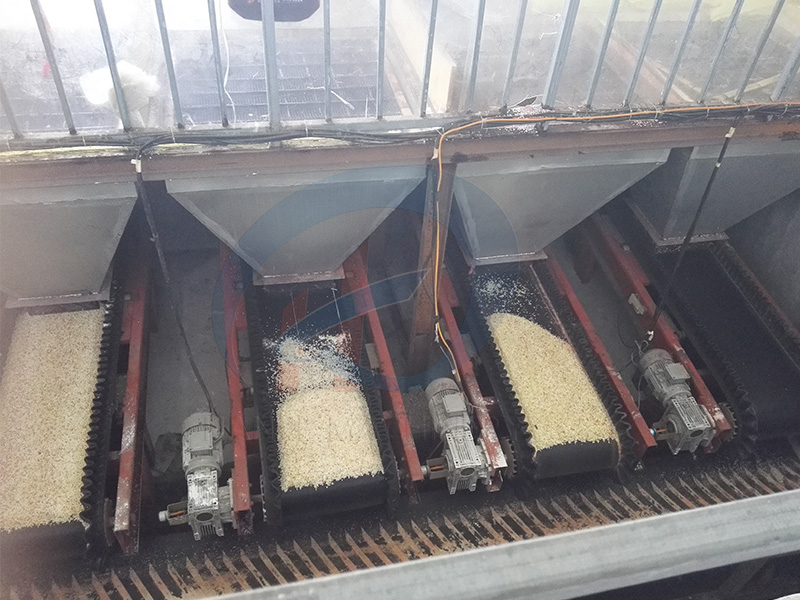

First, clarify "What is a mixing silo for?" "
Simply put, the compounding silo is the "raw material warehouse + precise weigher" of the organic fertilizer production line.
Raw material warehouse: Stores various raw materials (such as cow dung, straw powder, and mushroom strain powder).
Precise weigher: According to the formula ratio, different raw materials are added into the mixer in the prescribed quantities to ensure that the composition of each batch of fertilizer is consistent.
Ii. How to Match? Take it in three steps!
Step 1: Divide into "large and small silos" according to the amount of raw materials used
Raw materials are classified into three categories, and different sizes of warehouses are allocated according to the usage.
Large storage bins (for main materials) : For raw materials with a usage exceeding 50% (for example, cow dung accounts for 60%), two large storage bins are provided (to prevent material shortage, one is in use and the other is on standby).
Example: If 10 tons of fertilizer are produced per hour, 6 tons of cow dung are needed per hour. The silo should be able to store at least 8 hours of the amount (6×8=48 tons). Assuming the density of cow dung is 0.7 tons per cubic meter, the silo capacity is approximately 68 cubic meters (in reality, 80 cubic meters can be allocated, leaving a margin).
Medium warehouse (storage of auxiliary materials) : For raw materials with a usage of 5% to 50% (for example, 30% of straw powder), one medium warehouse is required.
Example: 3 tons of straw powder is needed per hour, and the warehouse capacity is approximately 34 cubic meters (50 cubic meters can be configured).
Small silo (for storing additives) : For raw materials with a usage of less than 5% (for example, 2% of the strain powder), prepare half a small silo (to prevent caking, prioritize the selected materials that have been properly added).
Example: The strain powder requires 0.2 tons per hour, and the warehouse capacity is approximately 4 cubic meters (10 cubic meters can be equipped, with an arched breaking device).
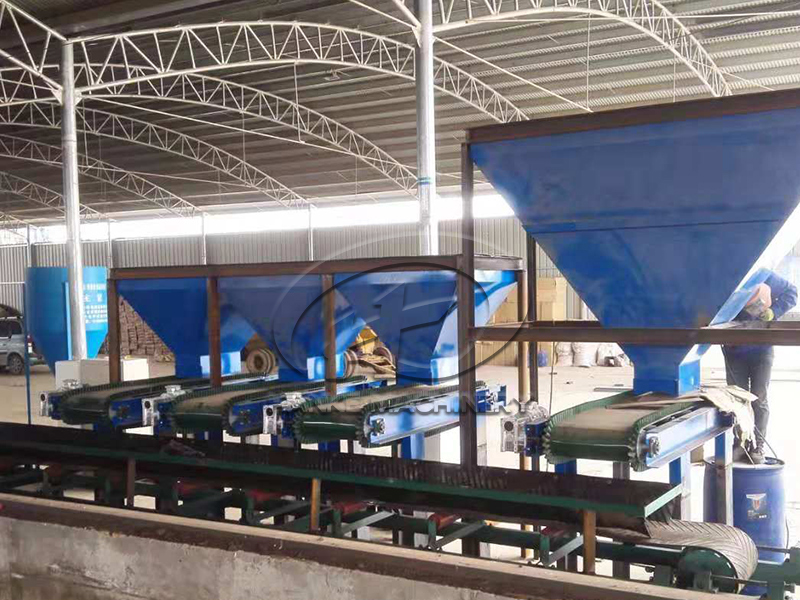
2. Step Two: The "shape" and "anti-clogging" design of the warehouse
The shape of the silo: The Angle of the cone should be steep enough (at least 50°, and 70° for damp raw materials like cow dung), otherwise the raw materials will get stuck at the bottom of the cone and cannot come out.
Anti-blocking wonder: Vibrator: Just like the vibration of a mobile phone, it shakes off the stuck raw materials (suitable for straw powder).
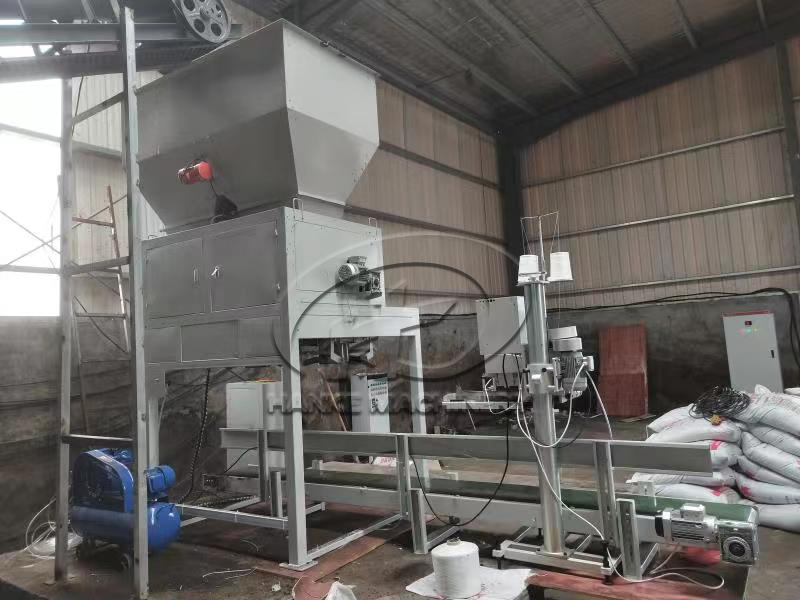
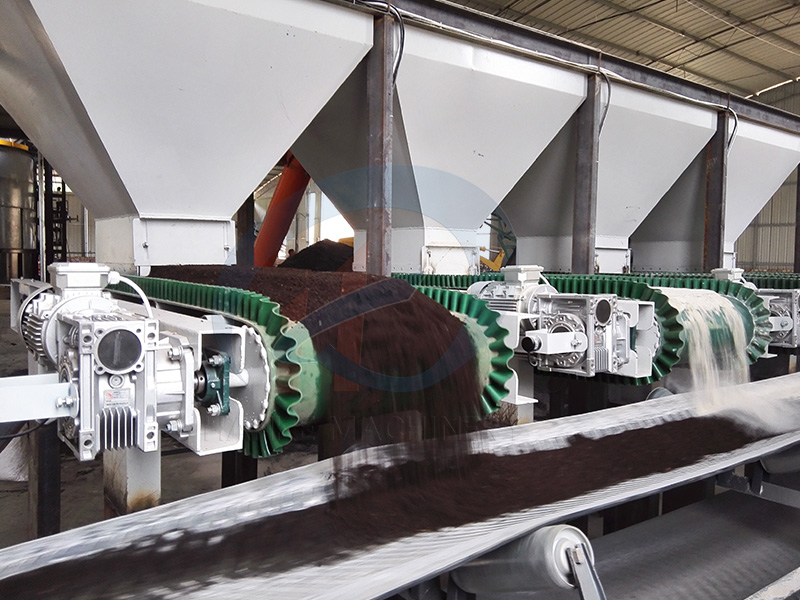
3. Step 3: Equip with "feeding + weighing" devices
Electronic belt scale: Raw materials are weighed on the belt, and the weight is displayed in real time (like weighing vegetables in a supermarket).
Loss-in-weight scale: Directly measures how much material is missing in the bin (suitable for small proportion raw materials).
Iii. Actual Case: How Do Small Factories Configure?
Scene: Annual production of 5,000 tons of powdered organic fertilizer, with the main material being cow dung (60%), the auxiliary material being straw powder (30%), and the additive being bacterial strain powder (5%) + trace elements (5%).
Configuration plan
The number and size of the warehouses
Cow dung silos: 2, each with a capacity of 80 cubic meters (capable of storing approximately 56 tons of cow dung, calculated at 0.7 tons per cubic meter).
Straw powder silo: 1, 50 cubic meters (capable of storing approximately 20 tons of straw powder, calculated at 0.4 tons per cubic meter).
Strain + trace element compartment: 1, divided into two compartments (15m³ per compartment, to prevent cross-contamination).
Iv. Guide to Avoiding Pitfalls
The storage bin should not be too small: the raw materials cannot be stored for 8 hours, and the production is intermittent (for example, the cow dung storage bin is only 50 cubic meters, but actually 80 cubic meters are needed).
Small proportion raw materials should be stored in separate warehouses: Do not mix the strain powder and trace elements in the same warehouse, as cross-contamination is likely to occur (for example, the strain may be "poisoned" by trace elements).
The raw materials should not be too wet: If the moisture content of the raw materials for powdered organic fertilizer is too high, they are prone to clumping in the warehouse, cannot be stirred well, and may even clog the discharge port. Therefore, the raw materials should be dried in the sun before preparation.
Don't fill the tank to the brim at once: Leave about one-third of the space for stirring. Otherwise, if the raw materials are too full, the mixer won't turn and the mixing effect will be poor.
After each mixing, clear the warehouse: Before the next batch of ingredients, clean up any remaining materials in the warehouse to prevent materials from different batches from mixing together and affecting the stability of the formula.
Summary
The configuration of the feeding silo = divided into large and small silos according to usage + anti-clogging design + precise feeding and weighing.
Small factories should first ensure "sufficiency and no congestion", and then gradually upgrade the accuracy. Big factories directly adopt automation, which is worry-free but expensive!

see details +

see details +
see details +

see details +

 Tel:+86 17319777703
Tel:+86 17319777703
 E-mail:hkautomaticpack@foxmail.com
E-mail:hkautomaticpack@foxmail.com
 Address:Xingyang City, Zhengzhou City, Henan Province.
Address:Xingyang City, Zhengzhou City, Henan Province.
Privacy Policy Copyright © Zhengzhou Hanke Machinery Equipment Co., Ltd Co., Ltd.